An Optical Fiber Cable (OFC) transmits data as light pulses through thin strands of glass or plastic, offering high bandwidth, long distances, and EMI immunity, making it ideal for modern internet, telecom, and data networks. These cables consist of a central core (glass/plastic) for light, surrounded by a cladding that reflects light back, protective layers (buffer, strength members), and an outer jacket, enabling faster, more secure communication than traditional copper cables.
Optical Fiber Cable
Overview
How it Works
- Light Transmission: Data (1s and 0s) is converted to light pulses by a transmitter.
- Total Internal Reflection: The core guides light, while the cladding reflects it inward, preventing signal loss over long distances.
- Reception: A receiver at the other end detects the light pulses and converts them back into electrical signals.
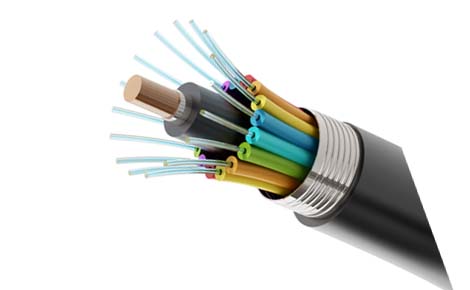
Key Components
- Core: The central, transparent part (glass or plastic) that carries light.
- Cladding: Surrounds the core, reflecting light back into the core via total internal reflection.
- Buffer Coating: A plastic layer protecting the fiber.
- Strength Members: Materials like aramid yarn (Kevlar) for tensile strength.
- Outer Jacket: The outermost protective layer against environmental damage (water, rodents).
